Eventing
Overview
What is it?
Eventing is a way to automatically perform actions based on some “event” within Mythic. The format and flow for this was heavily modeled after GitHub Actions, so if you’re familiar with that then this should come pretty easily.Components
There are a few components that make up an eventing workflow. Let’s see what happens when you click the “New Event Groups” but on on the left hand side and select a file/multiple files to upload:- The original eventing workflow file. This is a YAML, JSON, or TOML file that contains information about the entire workflow. In Mythic’s GraphQL API, each
eventgrouphas a file_id that points to this file so that the contents can always be fetched later. Clicking the image folder icon under “actions” will display this file in the UI. - After loading the workflow file and creating an
eventgroup, each step is analyzed and parsed into aneventstepassociated with that event group. - When an event happens and triggers a workflow, then an
eventgroupinstanceis created to track that specific instance along witheventstepinstancefor each step. This is how Mythic is able to tell all the different pieces from each other. These instances are tracked in the table below.
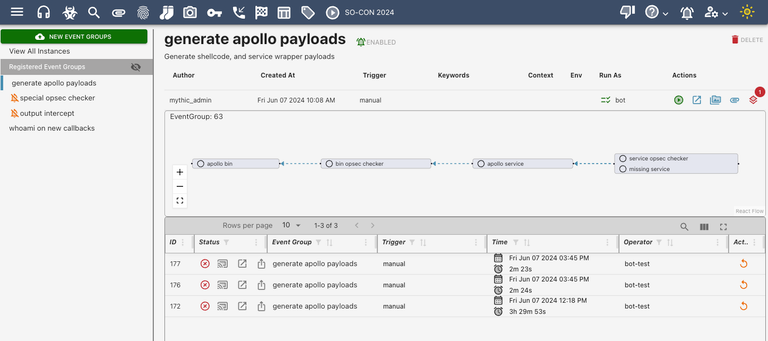
-
Author- this is the user that uploaded the workflow file -
Created At- this is when the user uploaded the workflow file -
Trigger- this is what “event” within Mythic will cause this workflow to execute -
Keywords- these are optional additional words you can use to kick off this workflow. For example, maybe you want something to execute each time there’s a new callback. However, as part of something else you’re doing, you want to execute this workflow anyway - you can associate a keyword with the workflow and then use that to execute the workflow at any time (more on that later). -
Context- this is additional context about the workflow to help decide if/when it should execute. For example, with the new callback trigger, you can use this context to limit which types of payloads you want to execute. A good example would be that you want to run some situational awareness commands when there’s a new callback, but you only want to do it for Windows payloads. This istrigger_datain Workflow Triggers. -
Env- this is extra, global data you can access and pass into all of the steps in a workflow. You can set this via theenvironmentkeyword. -
Actions- this is a set of additional actions you can take on this workflow -
If the trigger is
manualorkeyword, then thegreen playbutton will appear here and you can manually trigger this workflow. - The popout icon allows you to see the step flow graph in a bigger view
- The file image icon allows you to see the backing file for this workflow
- The paperclip icon allows you to upload additional files for this workflow. These files can then be referenced from within your steps (this is how, for example, you can handle issuing tasks that might need to upload files)
- The layered square icon gives context about additional services that might need to be running for this workflow to execute successfully. If this is red (with a number), then one or more additional services are needed (such as custom functions and conditional checks), but they’re offline.
- Graph: The big graph in the middle shows all the steps associated with this workflow and their dependencies. You can right-click any step and click “View Details” to get more contextual information about each specific step within the workflow overall.
A disabled event group workflow can’t run new instances, but still shows up by default in the UI. A deleted event group workflow can’t create new instance and doesn’t show up by default in the UI.